CRM Data Decay Rates by Industry: Complete Guide for 2026
Your sales team just spent the morning calling outdated phone numbers. Marketing’s email campaign bounced at a 12% rate. A major deal fell through because your contact changed companies three months ago and nobody updated the CRM. Sound familiar?
This isn’t a training problem or a process problem. It’s a data decay problem, and it’s costing your business more than you think. CRM data doesn’t just sit there unchanged. It degrades constantly. People change jobs, switch email addresses, move to new offices, and update phone numbers. Each change makes your carefully maintained database a little less accurate and a lot less valuable.
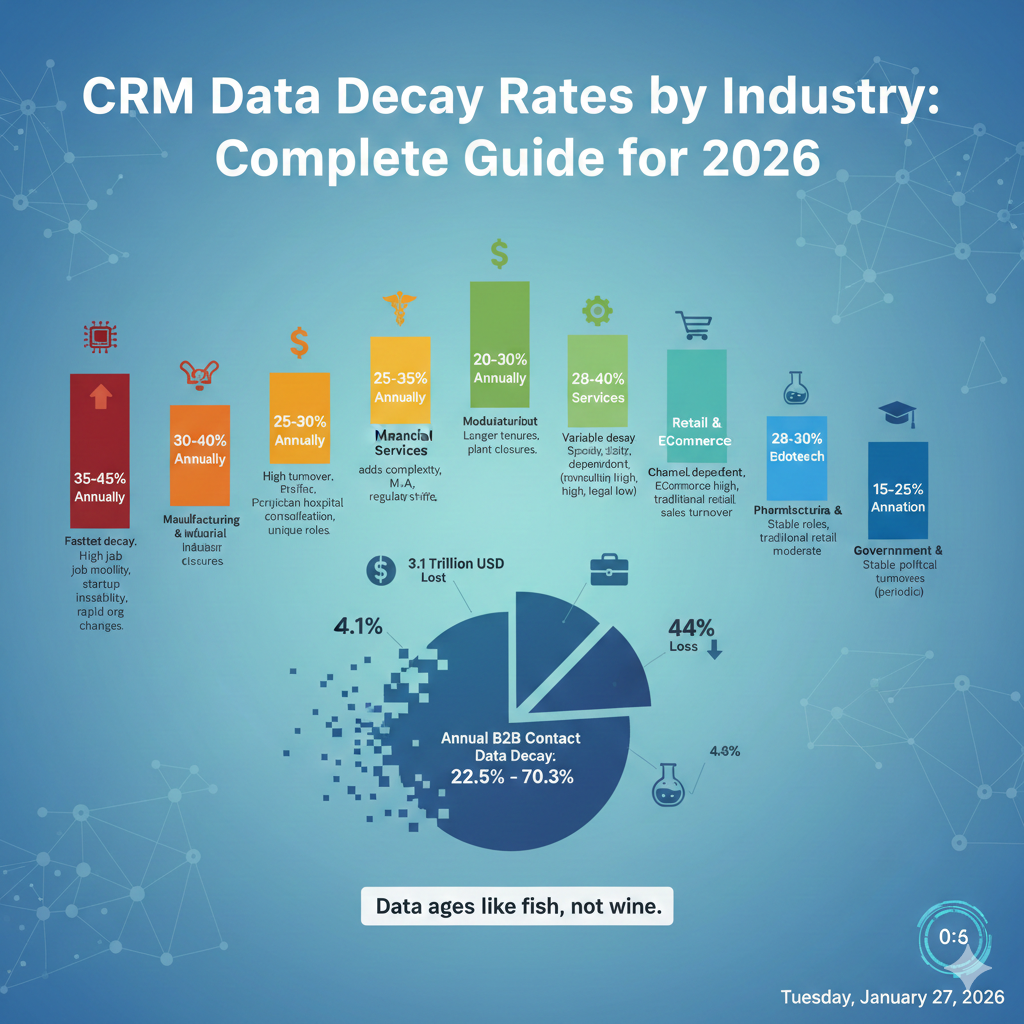
Here’s what makes it worse: decay rates aren’t uniform across industries. If you’re selling to technology companies, your database might be rotting at 40% annually. Healthcare contacts? Try 35% per year. Financial services? Around 30%. The industry you target directly impacts how quickly your CRM becomes obsolete.
According to recent research, B2B contact data decays between 22.5% and 70.3% annually depending on industry and contact type. That means in a database of 10,000 contacts, you could lose 2,250 to 7,030 valid records every single year. Each invalid record represents wasted time, blown opportunities, and damaged sender reputation.
The financial impact is staggering. Poor data quality costs U.S. businesses $3.1 trillion annually. Individual organizations lose $12.9 to $15 million per year through wasted marketing spend, lost sales opportunities, and operational inefficiencies. And 44% of companies experience annual revenue losses exceeding 10% specifically attributed to CRM data decay.
This guide breaks down CRM decay rates by industry, explains why certain sectors experience faster degradation, and shows you exactly how to fight back against data rot before it destroys your pipeline.
Understanding CRM Data Decay: What It Is and Why It Happens
CRM data decay is the gradual degradation of contact information accuracy over time. Your database starts clean on day one. Six months later, phone numbers don’t work. Email addresses bounce. Job titles are wrong. A year in, and nearly a quarter of your contacts might be completely invalid.
Three types of decay damage your CRM simultaneously.
Natural decay happens because people’s lives change. Employees switch jobs at a rate of 30% annually according to recent workforce data. When someone moves to a new company, their old work email stops working, their direct phone line disconnects, and their job title becomes irrelevant to your pitch. You did nothing wrong. The contact information just became obsolete naturally.
Mechanical decay occurs during data migration, system integration, or manual entry. When you import contacts from a spreadsheet into your CRM, fields get mismatched. Phone numbers land in email columns. First and last names flip. Duplicate records multiply. These technical glitches create immediate data quality problems that compound over time.
Organizational decay results from poor data governance. Sales reps create new contact records without checking for duplicates. Marketing downloads a list from a conference and imports it without verification. Nobody’s assigned to maintain data quality, so errors accumulate. This type of decay is entirely preventable but incredibly common.
The decay accelerates in predictable patterns. Month one, your data is 97% accurate. Next six months, you’re down to 85%. At month twelve, you’re at 75-78% depending on industry. By year two without maintenance, you might be operating with only 50-60% accurate data.
Contact types decay at different rates. Email addresses degrade faster than company information. Direct phone lines break more quickly than company switchboards. Job titles become outdated faster than company names. Understanding these patterns helps you prioritize verification efforts where they matter most.
Geographic factors influence decay speed. U.S. contact data tends to decay faster than European data due to higher job mobility rates. Asian markets show different patterns based on regional employment practices. If you sell globally, you’re dealing with multiple decay curves simultaneously.
Company size affects decay rates too. Startups and small businesses experience faster contact decay because of higher turnover and organizational instability. Enterprise accounts have more stable contact information but harder-to-navigate org charts. Mid-market companies fall somewhere in between.
The Great Resignation accelerated decay dramatically. According to Validity research, 79% of CRM users report that data decay has accelerated since COVID-19. Massive workforce shifts, remote work adoption, and organizational restructuring created unprecedented contact information churn.
Technology Industry: The Fastest CRM Decay Rates
Technology companies face the most aggressive CRM data decay in any industry. If you’re selling software, hardware, cloud services, or any tech product, you’re fighting annual decay rates between 35% and 45%. On contact lists focused on startups and high-growth tech companies, decay can reach 50% or higher annually.
Why does tech decay so fast? Job mobility. Technology professionals change jobs every 2-3 years on average, compared to 4-5 years in other industries. Software engineers get recruited constantly. Startup employees jump ship when funding runs out. Tech executives move between companies chasing the next opportunity.
Company instability drives additional decay. Startups fail at high rates. Acquisitions happen constantly. Company names change, domains shift, and entire organizations disappear. When a SaaS company gets acquired, every contact at that company potentially becomes invalid as email systems integrate and roles consolidate.
The pace of organizational change in tech is relentless. A technology company might reorganize quarterly, creating new departments, eliminating old ones, and shuffling responsibilities constantly. Job titles change. Reporting structures shift. The CTO you connected with six months ago might now be VP of Engineering, Chief Product Officer, or working at a completely different company.
Remote work intensified tech sector decay. Many technology companies went permanently remote, leading employees to relocate geographically. Office addresses changed. Direct phone lines disappeared. The contact information you had for a San Francisco-based engineer might now point to an Austin residence without forwarding.
Startup-specific decay patterns are brutal. A tech startup that raised Series A might have 50 employees. Eighteen months later, if they didn’t secure Series B funding, half the team could be gone. Your carefully cultivated relationships with product managers, engineers, and executives evaporate overnight.
High-growth companies create different decay patterns. A successful startup scaling from 100 to 500 employees in a year will see massive organizational changes. New layers of management appear. Early employees move into different roles. The contact who was director of everything is now focused on a narrow specialty, and five new directors handle what they used to do.
Technology buyer personas shift quickly. The person evaluating your software today might not be the buyer six months from now as the company matures and hiring progresses. Staying ahead of these shifts requires aggressive contact data maintenance and continuous prospecting.
Geographic concentration compounds the problem. Major tech hubs like San Francisco, Seattle, Austin, and Boston see constant talent circulation between companies. A software developer might work at three different startups in the same city over 5 years, creating multiple obsolete records in your CRM all pointing to the same person.
Tech companies typically need to verify contact data every 60-90 days to maintain acceptable accuracy. Quarterly verification is minimum. Monthly is better for active accounts and hot prospects.
Healthcare: High Decay with Unique Challenges
Healthcare experiences CRM data decay rates between 30% and 40% annually. The causes are complex and industry-specific, making healthcare contact databases particularly challenging to maintain.
Physician turnover drives significant decay. Doctors change practices, move between hospital systems, open their own clinics, or transition into administrative roles. When a cardiologist moves from a large hospital group to a smaller private practice, all their contact information changes—email address, phone number, physical location, and often even their prescribing patterns.
Hospital system consolidation creates massive contact information disruptions. When Hospital System A acquires Hospital System B, email domains change, phone systems integrate, and organizational charts restructure. Every administrator, physician, and staff member at the acquired facility potentially needs updated contact information.
Medical residents and fellows present unique decay challenges. These physicians move between institutions every 1-3 years as part of their training. Your database might have contact information for a resident at Mayo Clinic, but they’ve now completed their residency and started a fellowship at Johns Hopkins. The contact is still a physician, still a potential customer, but completely unreachable with your current data.
Nurse practitioners and physician assistants experience high mobility. These healthcare professionals frequently move between practices, especially early in their careers. PA decay rates can reach 40-45% annually in some specialties.
Hospital administrators and C-suite executives shift roles regularly. The Chief Medical Officer at a 500-bed hospital might move to a health system executive role, consulting position, or different institution. These high-value contacts require constant monitoring to maintain accuracy.
Academic medical center contacts decay through a combination of factors. Faculty physicians split time between clinical practice, research, and teaching. Their primary email might be university-based, but they also have a hospital email and possibly a private practice address. Determining which contact method is most effective requires ongoing verification.
Healthcare email configurations complicate decay management. Many hospital systems use catch-all email domains, making it difficult to verify whether specific physician addresses are still active. A bounced email doesn’t necessarily mean the doctor left the system—it might just mean the email format changed.
Medical licensing and credentialing data provides some stability. While contact information changes frequently, NPI (National Provider Identifier) numbers remain constant. Linking your CRM data to NPI registries helps track physicians even as they move between practices.
Specialty-specific decay patterns exist. Hospitalists and emergency medicine physicians move frequently. Established specialists in private practice show more stability. Primary care physicians in community practice tend to have lower decay rates than those in large medical groups.
Rural healthcare sees different decay rates than urban. Rural physicians and administrators change positions less frequently but face unique challenges like practice closures and consolidation that can wipe out entire contact lists suddenly.
Healthcare contact data requires quarterly verification at minimum. For active pharmaceutical sales territories or medical device sales lists, monthly verification is necessary to maintain pipeline quality.
Financial Services: Compliance Adds Complexity
Financial services industries experience CRM data decay rates between 25% and 35% annually. The numbers look better than tech or healthcare, but compliance requirements and regulatory considerations add complexity to data maintenance.
Banking sector employees move between institutions regularly. A commercial banker at Wells Fargo might move to Bank of America, JPMorgan, or a regional bank within 3-4 years. Relationship managers change firms chasing better compensation or broader client portfolios.
Wealth management and financial advisors show different patterns. Individual advisors switching firms often take clients with them, making tracking these moves critically important. When a financial advisor you’ve been working with leaves one wealth management firm for another, your relationship might transfer—but only if you catch the move quickly.
Insurance industry contacts face moderate decay. Insurance agents and brokers experience turnover, but established agents with book-of-business tend to stay put longer than other financial services professionals. Commercial insurance contacts show more stability than personal lines.
Fintech accelerates decay in financial services. Technology-driven financial companies combine the high mobility of tech workers with the regulatory environment of financial services. Contacts at fintech startups and digital banks experience tech-level decay rates (35-45%) while traditional bank contacts see more moderate decay (25-30%).
Regulatory changes drive organizational restructuring. When compliance requirements shift, financial institutions reorganize departments, create new roles, and eliminate old positions. The compliance officer you worked with might now have a different title, responsibilities, or employer entirely.
Mergers and acquisitions are constant in financial services. Regional banks get acquired by national institutions. Wealth management firms consolidate. Insurance brokerages merge. Each M&A event triggers contact information changes as systems integrate and duplicate roles get eliminated.
Private equity and venture capital contacts turn over at high rates. Associates and analysts move through these firms on 2-3 year cycles. Partners are more stable but still switch firms seeking better deal flow or compensation.
Geographic considerations matter in financial services. Major financial centers like New York, London, and Hong Kong see constant movement of talent between institutions. Regional financial services contacts show more stability but face higher risk of company consolidation.
Job title inflation complicates financial services databases. Today’s Vice President might be tomorrow’s Senior Vice President or Managing Director. Title changes don’t always mean role changes, but they impact how you should approach and message these contacts.
Compliance requirements affect data maintenance strategies. Financial services regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific rules govern how you can collect, store, and update contact information. You can’t simply scrape LinkedIn and update your database—proper consent and verification processes are required.
Financial services contact data benefits from quarterly verification. High-value accounts and active opportunities should be verified monthly. Annual verification is insufficient given the mobility and organizational change in this sector.
Manufacturing and Industrial: Moderate but Steady Decay
Manufacturing and industrial sectors experience more moderate CRM data decay rates between 20% and 30% annually. While slower than tech or healthcare, the steady degradation still demands active management.
Manufacturing company contacts show relative stability. Plant managers, production supervisors, and operations directors tend to stay in positions longer than professionals in faster-moving industries. Average tenure in manufacturing roles runs 5-7 years, roughly double the tech industry average.
Engineering contacts within manufacturing decay at different rates. Design engineers and R&D staff show higher mobility, moving between companies every 3-5 years. Plant engineers and maintenance managers demonstrate more stability, often staying 7-10+ years with a single employer.
Supply chain and procurement professionals face moderate turnover. These buyer personas are critical for B2B sales, and they change positions every 4-6 years on average. When a procurement manager moves, they often transition to a similar role at a competitor or customer, making the contact still valuable if you can track the change.
Industrial distribution and rep organizations show unique patterns. Distributor sales reps change employers but often cover the same geographic territory and customer base. Tracking these moves is essential for maintaining distribution channel relationships.
Family-owned manufacturing businesses have the lowest decay rates. Contacts at multi-generational family businesses, especially in leadership roles, show exceptional stability. These relationships can span decades with minimal contact information changes.
Publicly-traded manufacturing companies face more frequent leadership turnover. C-suite executives at large manufacturers move between companies, retire, or get recruited to other industries. The VP of Operations you’ve worked with for three years might suddenly jump to a private equity-backed competitor.
Plant closures and consolidations create sudden, complete decay. When a manufacturing facility shuts down, every contact at that location becomes immediately invalid. Industry consolidation makes these events increasingly common, requiring monitoring of company health and facility status.
Geographic factors influence manufacturing decay differently than other industries. Manufacturing contacts in the Rust Belt show different patterns than those in the Sun Belt. Regional economic conditions, labor availability, and industry health all impact how stable your manufacturing contacts remain.
Trade show contacts from manufacturing show high initial decay. Lists collected at manufacturing trade shows can experience 30-40% decay in the first year as attendees change roles, job seekers find positions, or consultants complete projects. However, contacts who remain valid after year one tend to be very stable long-term.
Technical specialization creates micro-patterns. Contacts in highly specialized manufacturing niches (aerospace, medical devices, semiconductors) show different decay rates than those in general manufacturing. Specialization often means fewer employers in a region, leading to more stable employment.
Manufacturing contact databases should be verified semi-annually at minimum. High-value accounts and active opportunities warrant quarterly verification. The slower decay rate makes annual verification insufficient but less critical than in faster-changing industries.
Professional Services: Variability Across Specialties
Professional services encompasses consulting, legal, accounting, marketing agencies, and similar businesses. CRM data decay rates vary significantly by specialty, ranging from 25% to 40% annually depending on the specific service type.
Management consulting shows relatively high decay at 30-38% annually. Consultants move between McKinsey, Bain, BCG, Deloitte, and smaller boutique firms regularly. Associates and analysts cycle through every 2-3 years. Even partners change firms seeking different client bases or expertise areas.
Legal profession contacts decay slower at 22-28% annually. Attorneys, especially partners, tend to stay with firms longer than other professional services. However, associates move more frequently, and the rise of boutique practices has increased lateral movement among experienced lawyers.
Accounting firms show moderate decay at 25-32% annually. The Big Four firms experience regular turnover of staff and senior associates. Partners demonstrate more stability but still move between firms or start their own practices. Tax season creates predictable contact availability patterns rather than decay.
Marketing and advertising agencies face high decay at 35-42% annually. Creative professionals, account managers, and digital marketers change agencies frequently. The agency world sees constant movement as professionals chase better clients, creative opportunities, or compensation.
HR and recruiting firm contacts experience 30-36% decay. Recruiters switch firms constantly, often taking client relationships with them. When your recruiting contact moves from Robert Half to a boutique firm, tracking that change is critical to maintaining the relationship.
Architecture and engineering (A&E) firms show 24-30% decay. Project-based work creates some mobility, but technical specialization provides stability. Licensed professionals (architects, professional engineers) change employers less frequently than other professional services contacts.
Career stage dramatically impacts decay in professional services. Junior-level professionals (analysts, associates, coordinators) have extremely high turnover—often 40-50% annual decay. Mid-level professionals show moderate decay. Senior partners and principals demonstrate the most stability.
Boutique versus large firm patterns matter. Contacts at large professional services firms (the Big Four, major consulting firms, national law firms) experience structured career progression that triggers role and title changes even when they stay with the same employer. Boutique firm contacts show more stability in role but higher risk of firm closure or merger.
Remote work impacted professional services decay. Many consulting and service firms went remote or hybrid, leading to geographic dispersion of teams. Office locations became less relevant. Direct phone lines disappeared. Email remains the most stable contact method.
Professional services contacts often maintain personal email addresses and LinkedIn profiles that provide secondary contact paths. When a consultant moves from Firm A to Firm B, their LinkedIn updates immediately. Building multi-channel contact strategies helps overcome professional services decay.
Partnership transitions create complex decay events. When partners leave to start their own firms, they often take teams with them. One senior departure can invalidate dozens of contact records simultaneously as associates and managers follow.
Professional services databases should be verified quarterly. Active prospects and ongoing relationships warrant monthly verification. The high mobility in this sector makes semi-annual verification insufficient for pipeline health.
Pharmaceutical and Biotech: Specialized Decay Patterns
Pharmaceutical and biotech industries experience CRM data decay rates between 28% and 38% annually. The unique nature of life sciences creates specialized decay patterns that require industry-specific management strategies.
Research scientists and principal investigators show moderate decay at 25-32% annually. Academic researchers move between universities, institutes, and industry positions. Postdocs advance to faculty positions or industry roles every 2-4 years. Senior PIs demonstrate more stability but still change institutions for better facilities, funding, or opportunities.
Pharmaceutical sales and medical affairs professionals face high turnover. Sales representatives change companies chasing better territories, products, or compensation. Average tenure in pharma sales runs 3-4 years. Medical science liaisons (MSLs) experience slightly lower turnover at 4-5 years but still create significant database decay.
Clinical research organization (CRO) contacts show elevated decay at 32-38% annually. Clinical research associates, project managers, and study coordinators move between CROs frequently. The contract-based nature of clinical trials drives mobility as professionals follow study opportunities.
Biotech startup employees experience tech-level decay. Early-stage biotech combines the high mobility of tech workers with the specialized science of life sciences. Contacts at pre-clinical and Phase 1 companies can see 40-45% annual decay as companies pivot, fail, or get acquired.
Hospital and health system contacts within pharma selling deserve special mention. When pharmaceutical companies target prescribers, they face the healthcare decay patterns discussed earlier (30-40% annually). The challenge compounds when selling to both physicians and hospital administrators simultaneously.
Regulatory and compliance professionals in life sciences show moderate stability at 24-30% decay. These specialized roles require specific expertise, creating somewhat lower mobility. However, movement between pharma, CRO, and consulting firms still occurs regularly.
Key opinion leaders (KOLs) and thought leaders in medicine present unique tracking challenges. These high-value contacts might be researchers, physicians, or clinicians whose influence spans years or decades. Their institutional affiliations change, but their value to pharmaceutical marketing remains. Tracking KOLs requires monitoring multiple data sources—publications, conference presentations, clinical trial involvement, and institutional affiliations.
Specialty pharma versus large pharma decay differently. Contacts at major pharmaceutical companies (Pfizer, Merck, J&J) show patterns similar to other large enterprises. Specialty pharma and rare disease companies experience higher decay as the smaller organizations grow, reorganize, or get acquired frequently.
Generic drug manufacturers and distributors face different decay patterns. These organizations operate more like traditional manufacturers, with corresponding moderate decay rates (25-30% annually). The sales and business development contacts show more stability than in branded pharma.
Medical device companies straddle pharma and manufacturing. Decay rates run 26-34% depending on device type and company size. Implantable device makers show patterns similar to pharmaceutical companies. Durable medical equipment contacts align more with manufacturing decay rates.
Pharmaceutical contact databases require quarterly verification at minimum. Active prescriber lists and KOL databases should be verified monthly. The high stakes and long sales cycles in pharma make data accuracy especially critical—a single invalid contact could mean losing access to a key decision-maker during a product launch.
Retail and eCommerce: Channel-Dependent Decay
Retail and eCommerce sectors experience CRM data decay rates between 28% and 40% annually, with significant variation based on whether you’re targeting B2B or B2C contacts and which channel you’re focused on.
Traditional retail buyer contacts show moderate decay at 26-32% annually. Category buyers, merchandise managers, and purchasing directors at major retailers change positions every 3-5 years. These contacts often move between retailers, shifting from Target to Walmart to Amazon or into retail consulting roles.
eCommerce and digital retail contacts face higher decay at 35-42% annually. The digital retail space mirrors tech industry mobility patterns. eCommerce directors, digital marketing managers, and online merchandising professionals move frequently between companies and often transition between retail and pure-play tech companies.
Retail store management contacts experience different patterns. Store managers, district managers, and regional directors show 30-36% decay. Store-level contacts change due to both personnel turnover and store closures as retail continues its difficult transformation.
Omnichannel retail decision-makers represent critical contacts with elevated decay. As retailers struggle to integrate online and offline operations, the professionals managing these initiatives move frequently—either advancing within their current organization, jumping to competitors, or shifting to consulting and technology vendors.
Retail technology and POS (point-of-sale) contacts show 32-38% decay. These specialized roles sit at the intersection of retail and technology, experiencing mobility patterns similar to tech industry contacts. When retailers undergo system upgrades or operational transformations, these contacts often change roles or companies.
Fashion and apparel retail has unique seasonal patterns. Buyers and planners in fashion retail show elevated decay (35-40% annually) due to the high-pressure, seasonal nature of the business. Misses in merchandising decisions often lead to professional moves.
Grocery and food retail contacts demonstrate more stability at 24-30% decay. The grocery sector experiences less disruption than general retail, and contacts show corresponding longevity. However, the growth of online grocery and rapid delivery is starting to accelerate decay in this traditionally stable sector.
Franchise and multi-unit retail owner contacts require special consideration. Franchisees can own locations for decades, making them some of the most stable retail contacts. However, franchise territories change hands through sales, creating sudden complete invalidation of contact information for specific locations.
Retail association and buying group contacts show low decay at 18-25% annually. These organizations serve as intermediaries for independent retailers, and their staff members demonstrate above-average tenure and stability.
Pop-up retail and direct-to-consumer brands create extreme decay challenges. These businesses often operate for short periods, and contacts associated with failed ventures immediately become invalid. The DTC brand landscape sees constant entry and exit, making any list of contacts decay rapidly.
B2B selling to retail faces different decay than B2C. If you’re selling software, services, or products to retailers, you’re tracking the B2B contacts discussed above. If you’re a brand selling through retail, your direct retail contacts show the same decay patterns, but your end consumer data (if you’re capturing it) has completely different characteristics outside the scope of this guide.
Retail contact databases should be verified quarterly for major accounts and active opportunities. Annual verification is insufficient given the industry disruption and personnel mobility. Technology and eCommerce contacts specifically warrant monthly verification due to their tech-like decay rates.
Government and Education: The Slowest Decay
Government and education sectors experience the slowest CRM data decay rates across all industries, typically ranging from 15% to 25% annually. However, these sectors present unique challenges that make decay management still essential despite the slower degradation.
Government employee contacts show remarkable stability at 15-22% annual decay. Civil servants, especially those with tenure protection, remain in positions for decades. A procurement officer at a federal agency might hold the same role for 10-15 years. This stability makes government contacts valuable long-term relationship opportunities.
However, political appointments create sudden decay events. When administrations change (federal, state, or local), appointed positions turn over completely. Directors, commissioners, and political staff all change simultaneously. These periodic mass turnovers require proactive monitoring of election cycles and appointment news.
K-12 education contacts show moderate decay at 20-27% annually. Teachers and principals move between schools, change districts, or leave education entirely. Superintendent and administration turnover happens more frequently than you might expect—average superintendent tenure is only 3-4 years in many districts despite the apparent stability of the education sector.
Higher education contacts vary by role. University professors with tenure show exceptional stability—annual decay rates of 12-18%. They might change universities, but these moves are typically well-publicized and easy to track. University administrators (deans, provosts, presidents) face higher turnover at 25-35% annual decay as they move between institutions or into emeritus roles.
Research grant administration and sponsored research contacts at universities show 22-28% decay. While lower than corporate sectors, it’s elevated compared to faculty. These professionals move between universities more frequently than tenured professors.
Education technology contacts face elevated decay at 28-35% annually. School districts and universities hire education technology coordinators, instructional technologists, and similar roles that combine education and technology—and these positions see tech-industry levels of mobility.
Government contractors and consulting firms selling to government experience different decay patterns. The government employees they sell to show low decay, but the consultant’s own company contacts face professional services decay rates (25-35% annually).
Military contacts present unique situations. Active duty military personnel rotate positions every 2-4 years by design. A contracting officer at one base will eventually transfer to another base or role. However, their role is backfilled by another person in the same position, making the position itself stable even as individuals change.
State and local government shows higher decay than federal. Local government employees experience less job security, face more political pressure, and have more opportunities to move between municipalities. County and city employees show 22-28% decay compared to federal government’s 15-22%.
Non-profit and NGO contacts aligned with government show moderate decay at 23-30% annually. These organizations face funding instability and mission drift, leading to personnel changes. However, passionate mission-driven employees often stay longer than corporate counterparts.
Government and education databases can be verified semi-annually for most contacts. Active opportunities and high-value accounts warrant quarterly verification. The slow decay makes annual verification marginally acceptable but still risky for important relationships. Federal government contacts specifically can often operate on annual verification cycles with acceptable accuracy maintenance.
The Real Cost of CRM Data Decay
Understanding decay rates by industry matters because the costs are tangible and massive. Let’s break down exactly what decayed CRM data is costing your organization.
Wasted sales time is the most immediate cost. Your sales representatives spend hours each week calling disconnected numbers, emailing bounced addresses, and following up on contacts who left their companies months ago. Industry data shows that 50% of sales time is wasted on unproductive prospecting. Even if only half of that waste comes from decayed data, you’re losing 25% of sales productivity—effectively paying salespeople to chase ghosts.
Calculating this for your team. If you have 10 sales reps earning $100,000 each (total comp), 25% waste equals $250,000 in salaries paying for fruitless outreach. Add in lost opportunity cost – the deals they could have closed if focused on valid contacts – and the number multiples.
Marketing budget waste compounds the problem. Email campaigns sent to 30% decayed lists see bounce rates of 8-15%, damaging sender reputation and reducing inbox placement for all future campaigns. If you’re spending $500,000 annually on email marketing and 30% of your database is invalid, you’re wasting $150,000 sending messages that never arrive.
Lead generation costs multiply when lists decay. You pay $50-$200 per lead to generate new contacts. If those contacts decay at 30% annually and you don’t replace them, you need to generate 30% more leads just to maintain database size. At 1,000 leads per year, that’s 300 additional leads required, costing $15,000-$60,000 extra.
Revenue losses hit hardest. Research shows that 44% of companies experience annual revenue losses exceeding 10% specifically attributed to CRM data decay. For a $10 million revenue company, that’s $1 million in lost sales directly traceable to outdated contact information. The deal that falls through because your champion changed companies. The expansion opportunity you missed because the contact information was six months old.
Customer relationships suffer. When you send communications to the wrong person or wrong address, you damage brand perception. The replacement contact at the company sees that you’re not tracking their organization properly. Your attention to detail and professionalism come into question.
Pipeline accuracy becomes fiction. When 25-40% of your contacts are outdated, your pipeline forecasts are fundamentally flawed. You think you have $5 million in qualified opportunities, but $1.5 million of that pipeline is built on contacts who are no longer in role. Your quarterly forecasts miss. Executive confidence in your projections erodes.
Reporting and analytics mislead. You’re making strategic decisions based on data that’s 30% incorrect. Which industries should you target? What size companies convert best? Your analysis is polluted by decayed data, leading to poor strategic choices that waste resources for years.
Compliance risks emerge in regulated industries. In financial services, healthcare, and government contracting, maintaining accurate contact records isn’t just good practice—it’s often required by regulation. Persistent contact information errors can create compliance violations with financial penalties.
The compound effect kills. All these costs interact and multiply. Wasted sales time leads to missed revenue. Marketing inefficiency requires more lead generation spending. Poor analytics drive bad strategy. Each year of ignored decay adds another layer of cost and inefficiency.
According to Gartner research, poor data quality costs organizations an average of $15 million annually. For smaller businesses, scale that down proportionally – a $10 million revenue company might face $150,000-$300,000 in annual costs from poor data quality, much of it driven by decay.
These aren’t one-time costs. They recur every single year that decay goes unaddressed. Over five years, a mid-market company could easily lose $1-2 million to decayed CRM data. That’s real money that could fund expansion, hire additional sales reps, or drop directly to the bottom line.
Advanced Strategies to Combat CRM Decay
Fighting CRM decay requires more than just occasional list cleaning. The most successful organizations implement comprehensive data maintenance strategies that address decay continuously.
Automated data enrichment services continuously update contact information in the background. These systems monitor job changes, company updates, and contact information shifts across multiple data sources. When someone in your CRM changes jobs, the system detects it within days and flags the record for review or automatically updates it based on verification rules you set.
Real-time verification at point of entry prevents bad data from entering your CRM in the first place. When a sales rep adds a new contact, verification APIs instantly check whether the email address is valid, the phone number is properly formatted, and the company information is accurate. Invalid data gets flagged immediately for correction before it pollutes your database.
Engagement tracking identifies decayed contacts proactively. Contacts who haven’t opened an email in 6 months, never answered calls, and show no website activity are likely invalid even if they haven’t bounced. Automated scoring flags these dormant contacts for verification or suppression well before they damage campaign performance.
Quarterly verification cycles should be mandatory, not optional. Build verification into your quarterly business review process. Every 90 days, run your entire active database through verification services. Flag records with issues, assign them to account owners for research, and update or suppress as needed.
Specialized verification for high-value accounts matters more than bulk list cleaning. Your top 100 accounts represent 60-80% of your revenue. Assign someone to manually verify these critical contacts monthly. Check LinkedIn, review company websites, and call to confirm information. The ROI on maintaining accuracy for your biggest opportunities is enormous.
AI and machine learning models can predict decay before it happens. Advanced systems analyze patterns – contacts at companies going through M&A are likely to change. Contacts in roles with historically high turnover should be verified more frequently. Predictive scoring helps you focus verification efforts where decay is most likely.
Integration between CRM and data providers automates maintenance. Services like ZoomInfo, Clearbit, and Cognism offer integrations that continuously refresh contact data in your CRM. When they detect a job change, the information flows directly into Salesforce or HubSpot without manual intervention.
Role-based verification frequencies help optimize resources. C-suite contacts at Fortune 500 companies might only need annual verification because they’re stable and well-tracked publicly. Contacts in startups need monthly verification. Tailor your verification schedule to decay risk.
Duplicate detection and merging prevents mechanical decay. Regular deduplication runs identify and merge duplicate contact records before they cause confusion. Modern deduplication uses fuzzy matching to catch duplicates even when information doesn’t match exactly – catching that John Smith and J. Smith are the same person despite different email addresses.
Team accountability builds a data quality culture. Assign data quality metrics to sales and marketing leadership. Track decay rates by team or territory. Recognize and reward teams that maintain clean data. Make data quality part of performance reviews and compensation where appropriate.
Source tracking helps identify bad data sources. Tag every contact in your CRM with how they entered the database – trade show, inbound lead, purchased list, manual entry, partner referral. When you identify high decay rates from a particular source, you can adjust purchasing or collection strategies.
Sunset policies automatically suppress severely decayed contacts. If a contact hasn’t responded to email in 12 months, has bounced multiple times, never answered calls, and shows no activity, suppress them from active campaigns. Don’t delete (historical context has value), but stop wasting resources pursuing ghosts.
Re-engagement campaigns help identify which dormant contacts are actually still valid. Before suppressing inactive contacts entirely, run a targeted “are you still there?” campaign. Some percentage will respond, confirming they’re valid but just not currently in market. You’ve saved contacts that traditional decay metrics would have classified as invalid.
Purchase validated data from specialized providers rather than cheap bulk lists. SparkDBI’s verified healthcare professional databases and B2B contact lists are maintained with continuous verification processes. Buying pre-verified data costs more upfront but saves enormous amounts in wasted outreach and damage control.
Mobile phone and SMS verification adds another contact channel that often outlasts email. People change jobs but keep personal mobile numbers. Adding verified mobile contacts to your CRM provides a decay-resistant secondary contact method. When work email fails, texting often still reaches the person.
LinkedIn Sales Navigator integration keeps your CRM updated with publicly available information. When contacts update their LinkedIn profiles with new job titles, companies, or locations, those changes can flow into your CRM. This isn’t perfect (people don’t always update LinkedIn immediately), but it catches many changes automatically.
The key insight across all these strategies: fighting CRM decay requires systematic, continuous effort. One-time list cleaning provides temporary relief but doesn’t solve the underlying problem. Organizations that win on data quality treat decay prevention as an ongoing process, not an annual project.
How SparkDBI Addresses CRM Decay in Healthcare and B2B Data
SparkDBI specializes in maintaining clean, accurate contact databases in the face of persistent data decay. Our approach combines automated verification, human research, and continuous monitoring to deliver contact lists that stay accurate over time.
Our healthcare professional (HCP) databases address the unique 30-40% annual decay rates in medical fields. We verify physician email addresses, phone numbers, practice locations, and specialty classifications quarterly at minimum. High-value prescribers and key opinion leaders in our databases receive monthly verification to ensure pharmaceutical and medical device companies always have current contact information.
We track physician movements between practices, hospital systems, and academic institutions. When a cardiologist moves from one medical group to another, our verification processes catch the change within 30 days. Our clients don’t waste time and budget sending campaign materials to outdated addresses.
NPI (National Provider Identifier) validation is core to our healthcare verification. By linking contact records to verified NPI numbers, we can track individual physicians even as their practice affiliations change. This approach dramatically reduces the impact of decay on healthcare contact databases.
Our B2B contact verification services extend across all industries covered in this guide—technology, finance, manufacturing, professional services, and retail. We understand that tech contacts decay at 40% while manufacturing decays at 25%, and we apply appropriate verification frequencies to each industry segment.
Multi-source verification ensures accuracy. We don’t rely on a single data source. Our verification process checks contact information against public records, business databases, professional licensing boards, company websites, and activity signals. When multiple sources confirm the same information, confidence in accuracy increases dramatically.
Real-time verification APIs integrate with your CRM platform. As sales reps add new contacts to Salesforce, HubSpot, or other systems, our API instantly verifies the information and returns data quality scores. Invalid entries get flagged immediately, preventing bad data from entering your database.
Bulk list verification services help you clean existing databases. Upload your current CRM export, and we’ll verify every contact, flag decay issues, identify duplicates, and append missing information where available. Most verification projects are completed within 24-48 hours, allowing you to quickly restore database quality.
We provide decay scoring that predicts which contacts are most likely to become invalid soon. This probabilistic approach helps you prioritize verification efforts where decay risk is highest. A contact at a recently acquired company gets a high decay risk score. Someone who’s been in the same role at a stable company for eight years gets a low score.
Continuous monitoring services track your most valuable contacts automatically. For your top 100 or top 1,000 accounts, we can set up automated monitoring that checks contact information monthly or even weekly. When changes are detected, you receive alerts immediately, allowing proactive relationship management before the contact information becomes completely invalid.
Campaign-level verification right before send protects deliverability. Before you launch a major email campaign, we verify the target list to identify any recent decay. This final check catches last-minute job changes and prevents bounces that damage sender reputation.
Our data enrichment services don’t just verify existing information – we append missing data. If you have an email address but no phone number, we’ll find it. If you have a company name but no decision-maker contacts, we’ll identify them. Enrichment fills the gaps that make CRM records more useful.
HIPAA compliance, SOC 2 certification, and GDPR alignment protect your data and ours. Healthcare data requires special handling, and our processes meet the strict requirements of medical data management. Your contact verification doesn’t expose you to compliance risks.
Custom verification workflows fit your specific needs. Different organizations have different risk tolerances and budget constraints. We build verification programs that match your requirements—whether that’s monthly verification of all contacts, quarterly verification with monthly high-value account checks, or fully automated continuous verification.
The result: SparkDBI clients maintain database accuracy rates of 92-96% even in high-decay industries like technology and healthcare. While competitors struggle with 70-75% accuracy as decay erodes their lists, our clients operate with confidence that their contact information is current and their outreach will connect with real decision-makers.
Industry-Specific Verification Best Practices
Different industries require different verification strategies. One-size-fits-all approaches miss the nuances that make industry-specific decay management effective.
Technology sector best practices: Verify monthly for startups and high-growth companies. Verify quarterly for established tech firms. Monitor funding announcements, acquisition news, and layoff reports – these events trigger immediate decay spikes. Focus on LinkedIn as a primary source for job change intelligence in tech, as professionals in this sector update profiles quickly.
Healthcare verification priorities: Cross-reference against medical licensing databases and NPI registries. Verify specialty classifications beyond just contact information – a physician’s specialty affects which pharmaceutical and device campaigns they should receive. Track hospital system M&A news, as acquisitions create massive contact information shifts. Don’t overlook mid-level providers (NPs and PAs) who decay faster than physicians.
Financial services considerations: Monitor regulatory announcements for compliance-driven organizational changes. Verify quarterly for relationship-based roles (relationship managers, financial advisors, wealth managers). Annual verification is marginally sufficient for back-office and operations contacts. Track M&A obsessively – financial services consolidation happens constantly and invalidates contacts at scale.
Manufacturing verification strategies: Semi-annual verification works for most manufacturing contacts due to moderate decay rates. Prioritize verification for engineering and procurement contacts who change more frequently than operations staff. Monitor plant closure announcements and industry consolidation news. Build longer-term relationships knowing manufacturing contacts typically stay in role 5-7 years.
Professional services tactics: Verify quarterly across all professional services contacts due to 25-40% decay. Track promotions and title changes aggressively – these roles have clear advancement tracks that create title churn even when people stay with the same firm. Monitor boutique firm launches, as senior professionals leaving big firms to start their own practices create sudden contact information changes.
Pharmaceutical and biotech strategies: Separate verification strategies for researchers versus commercial contacts. Researchers can be verified semi-annually. Sales and medical affairs professionals need quarterly verification. Track clinical trial progress for CRO contacts, as study milestones often trigger team changes. Monitor FDA approvals and pipeline developments, as these events drive organizational changes.
Retail and eCommerce priorities: Verify technology and digital contacts monthly (they follow tech decay patterns). Verify traditional retail buyers and merchandising contacts quarterly. Track store closure announcements and retail bankruptcies religiously. Don’t invest heavily in verifying store-level management unless that’s your specific target – the high decay and company instability makes maintaining accuracy difficult.
Government and education approaches: Annual verification is acceptable for tenured faculty and career civil servants. Verify administrator and political appointment contacts quarterly. Track election cycles aggressively – political changeovers create sudden mass decay events. Monitor university president and superintendent changes through higher education and K-12 news sources.
Cross-industry principles: Always verify before major campaigns. Always verify before engaging expensive resources like field sales or executive outreach. Always track your industry’s key information sources – industry publications, conference announcements, LinkedIn, company press releases. Set calendar reminders based on your industry’s decay rate rather than waiting for obvious signs of list problems.
Measuring and Reporting on Data Quality
You can’t manage what you don’t measure. Implementing data quality metrics and regular reporting helps maintain executive support for decay prevention investments.
Calculate your current decay rate quarterly. Take your total active contacts at quarter start. Track how many become invalid during the quarter (bounced emails, wrong phone numbers, left company). Divide invalid by total for your quarterly decay percentage. Multiply by four for annual decay rate. This baseline helps you track whether verification efforts are working.
Track verification return on investment. Calculate money spent on verification services. Calculate money saved from improved campaign deliverability, reduced sales waste, and recovered opportunities. Even rough estimates will show massive positive ROI – typically 10:1 or better for organizations with significant decay problems.
Monitor bounce rates by industry segment in your database. If you sell to multiple industries, track whether healthcare contacts bounce more than manufacturing contacts. This validates whether your verification frequencies match the actual decay patterns you’re experiencing.
Measure sales rep productivity on verified versus unverified contacts. Track call connection rates, email response rates, and meeting conversion rates. Contacts that have been recently verified should show significantly better response rates than contacts verified more than 6 months ago. This data builds internal support for verification investment.
Report on opportunity and revenue by data quality tier. Segment your pipeline into “verified within 90 days,” “verified 90-180 days ago,” and “not recently verified.” You’ll likely find that recently verified contacts generate disproportionate pipeline and revenue. This insight justifies continuous verification spending.
Track time-to-close by contact data quality. Deals built on recently verified, accurate contact information should progress faster than those hampered by outdated data. Quantifying this impact shows executives how data quality directly affects cash flow.
Create a data quality dashboard for executive review. Monthly or quarterly reports should show: total contacts in CRM, percentage verified within 90 days, estimated decay rate, bounce rate trends, and verification ROI. Keep it simple and visual – executives don’t need detailed methodology, just clear trends and business impact.
Benchmark against industry standards. Share this guide’s industry-specific decay rates with leadership. Show where your organization’s decay rate falls relative to industry averages. If you’re experiencing 45% decay in technology when the average is 35-40%, that indicates either poor verification practices or an unusually high-risk contact segment that needs addressed.
Assign accountability metrics. Marketing should own overall database quality metrics. Sales should own contact accuracy for their assigned accounts. Set targets (maintain 92%+ accuracy rate) and track performance quarterly. Data quality can’t be treated as someone else’s problem—it requires shared ownership.
The Future of CRM Data Decay Management
Data decay isn’t going away, but how organizations combat it is evolving rapidly. Understanding where the technology and best practices are heading helps you prepare for what’s next.
AI-powered predictive decay models are becoming mainstream. Instead of verifying all contacts on the same schedule, machine learning systems will predict which specific contacts are most likely to have decayed based on patterns, historical data, and external signals. Your CRM will flag contacts for verification based on actual decay risk, not arbitrary time intervals.
Real-time data verification will become standard. Rather than batch processing verification quarterly, systems will continuously verify contact information in the background. The moment a contact changes jobs or updates information somewhere on the internet, your CRM will catch it within hours or days, not months.
Blockchain-based contact verification might emerge. Decentralized identity verification systems could allow contacts to manage their own professional information in a verified, portable format. When someone changes jobs, they update their blockchain identity once, and all the databases that reference them update automatically. This remains speculative but addresses privacy and accuracy simultaneously.
Integration density will increase. Your CRM won’t just integrate with one or two data sources – it will pull from dozens simultaneously, cross-referencing information to validate accuracy. The more data sources confirm the same contact information, the higher the confidence score.
Privacy regulations will complicate but ultimately improve decay management. GDPR, CCPA, and emerging data privacy laws are forcing organizations to be more thoughtful about data collection and maintenance. The unintended benefit: companies will maintain smaller, higher-quality contact databases rather than massive poorly-maintained lists. This aligns perfectly with decay management best practices.
Mobile and alternative contact channels will matter more. As work email becomes less reliable (remote work, job changes, catch-all domains), mobile phone numbers, LinkedIn messaging, and other channels will become primary contact methods. Future CRM systems will treat email as one channel among many rather than the primary identifier.
Human-AI hybrid verification will become standard. Fully automated verification handles routine updates. Human researchers verify high-value contacts and resolve ambiguous cases. This hybrid approach combines automation efficiency with human judgment for optimal accuracy.
Industry-specific verification tools will proliferate. Rather than generic contact verification services, specialized tools for healthcare, financial services, manufacturing, and other industries will emerge. These tools will understand industry-specific decay patterns and data sources, delivering higher accuracy than general-purpose verification.
The trend is clear: decay management is moving from periodic batch cleaning toward continuous, intelligent, automated maintenance. Organizations that adopt these emerging approaches early will maintain competitive advantages through superior contact data accuracy.
Taking Action: Your 30-Day Decay Management Plan
Understanding CRM decay is valuable only if you act on it. Here’s a practical 30-day plan to assess and address decay in your organization.
Week 1: Assessment
Day 1-2: Run your entire CRM through a verification service to establish baseline accuracy. Note total contacts, percentage flagged as invalid, and percentage flagged as catch-all or risky.
Day 3: Calculate your estimated annual decay rate by industry segment. Use the rates in this guide as benchmarks.
Day 4-5: Analyze your last quarter’s email campaigns. Calculate bounce rates, complaint rates, and engagement rates. These metrics reveal decay’s impact on your current operations.
Week 2: Prioritization
Day 6-7: Identify your top 100 accounts by revenue potential. Manually research each key contact. Check LinkedIn, company websites, and Google News. Note how many contacts are no longer in role or at the company.
Day 8-9: Calculate the cost of decay for your organization. Use the formulas earlier in this guide: wasted sales time, marketing budget waste, lost revenue. Put a dollar figure on the problem to justify solutions.
Day 10: Present findings to leadership. Show the baseline accuracy, estimated decay rate, and cost calculations. Secure budget approval for verification services and ongoing maintenance.
Week 3: Implementation
Day 11-12: Select verification services and tools. If you need healthcare-specific verification, SparkDBI offers comprehensive HCP database verification. For cross-industry needs, evaluate options based on your specific industry mix.
Day 13-15: Implement verification workflows. Set up CRM integrations, establish verification schedules by industry/contact tier, and assign accountability to team members.
Day 16-17: Create data quality policies. Document verification frequencies, contact update procedures, duplicate management rules, and sunset policies for severely decayed contacts.
Week 4: Training and Rollout
Day 18-20: Train sales and marketing teams on new data quality procedures. Explain what decay is, why it matters, how verification works, and what their responsibilities are.
Day 21-23: Begin first full verification cycle. Process your entire database through your selected verification services. Create work queues for contacts that need manual research.
Day 24-25: Set up ongoing monitoring and reporting. Create dashboards that track data quality metrics. Schedule quarterly reviews.
Day 26-30: Review initial results and adjust. Assess which contacts were caught by verification. Refine your processes based on what you’ve learned.
Beyond 30 days: Maintain the discipline. Verification only works if it’s consistent. Stick to your quarterly verification schedules. Check high-value accounts monthly. Continuously improve your processes based on results.
Conclusion: Data Decay is Inevitable, But Manageable
CRM data decay is a fact of business life. People change jobs. Companies restructure. Contact information becomes obsolete. You can’t stop decay – but you can manage it effectively enough to maintain competitive advantage.
The industry you target determines how aggressive you need to be. Technology companies face 35-45% annual decay and need monthly or quarterly verification. Government contacts see only 15-22% decay and can operate on annual verification cycles. Understanding your specific industry’s decay patterns lets you build efficient verification strategies that maintain accuracy without overspending.
The cost of ignoring decay is too high to accept. Organizations lose $12.9 to $15 million annually on average from poor data quality, much of it driven by decay. Individual companies see 10%+ revenue losses attributed directly to outdated contact information. Your competitors who solve this problem will reach more prospects, close more deals, and grow faster than you.
The solution isn’t complicated, but it requires commitment. Regular verification on industry-appropriate schedules. Automated tools that catch changes quickly. Clear accountability for data quality. Continuous monitoring rather than annual cleanup projects. Organizations that implement systematic decay management maintain 92-96% database accuracy while competitors struggle at 70-75%.
SparkDBI brings industry expertise and verification technology together to help you win the battle against data decay. Our healthcare professional databases stay accurate despite 30-40% industry decay rates because we verify continuously and understand medical industry dynamics. Our B2B verification services adapt to the specific decay patterns of technology, financial services, manufacturing, and professional services industries.
The organizations that will dominate their markets over the next five years are those that maintain superior data quality. When your database is 95% accurate and your competitor’s is 70% accurate, you reach 35% more decision-makers with every campaign. You waste dramatically less sales time. Your pipeline forecasts are reliable. Your marketing budget delivers real ROI.
Data decay represents both a threat and an opportunity. The threat: left unmanaged, it slowly destroys your ability to reach prospects and customers. The opportunity: solving decay when competitors don’t creates a sustainable competitive advantage that compounds over tim$e.
Ready to take control of your CRM data quality? Contact SparkDBI to discuss industry-specific verification strategies, database health assessments, and ongoing decay management programs that keep your contact data accurate even as industries and organizations evolve.
